
Nuclear Medicine

Nuclear Medicine
Services

Ultrasound Thyroid
Thyroid ultrasound examines thyroid gland size, structure, and potential nodules or cysts.

Ultrasound Thyroid
Thyroid ultrasound examines thyroid gland size, structure, and potential nodules or cysts.

Cardiac scintigraphy
Cardiac scintigraphy (also known as myocardial perfusion) is a non-invasive and extremely gentle examination method for imaging the blood flow in the heart muscle - in contrast to cardiac catheterization. In this way, incipient circulatory disorders (ischemia) can be detected at an early stage and known coronary heart disease can be reliably monitored.

Cardiac scintigraphy
Cardiac scintigraphy (also known as myocardial perfusion) is a non-invasive and extremely gentle examination method for imaging the blood flow in the heart muscle - in contrast to cardiac catheterization. In this way, incipient circulatory disorders (ischemia) can be detected at an early stage and known coronary heart disease can be reliably monitored.

Thyroid scintigraphy (+ suppression)
Thyroid scintigraphy (+ suppression) gently visualizes functional disorders and enables targeted therapy planning. It shows which thyroid nodules absorb a lot or little iodine. This allows harmless “hot” nodules to be distinguished from suspicious “cold” nodules - often saving unnecessary punctures or operations.

Thyroid scintigraphy (+ suppression)
Thyroid scintigraphy (+ suppression) gently visualizes functional disorders and enables targeted therapy planning. It shows which thyroid nodules absorb a lot or little iodine. This allows harmless “hot” nodules to be distinguished from suspicious “cold” nodules - often saving unnecessary punctures or operations.
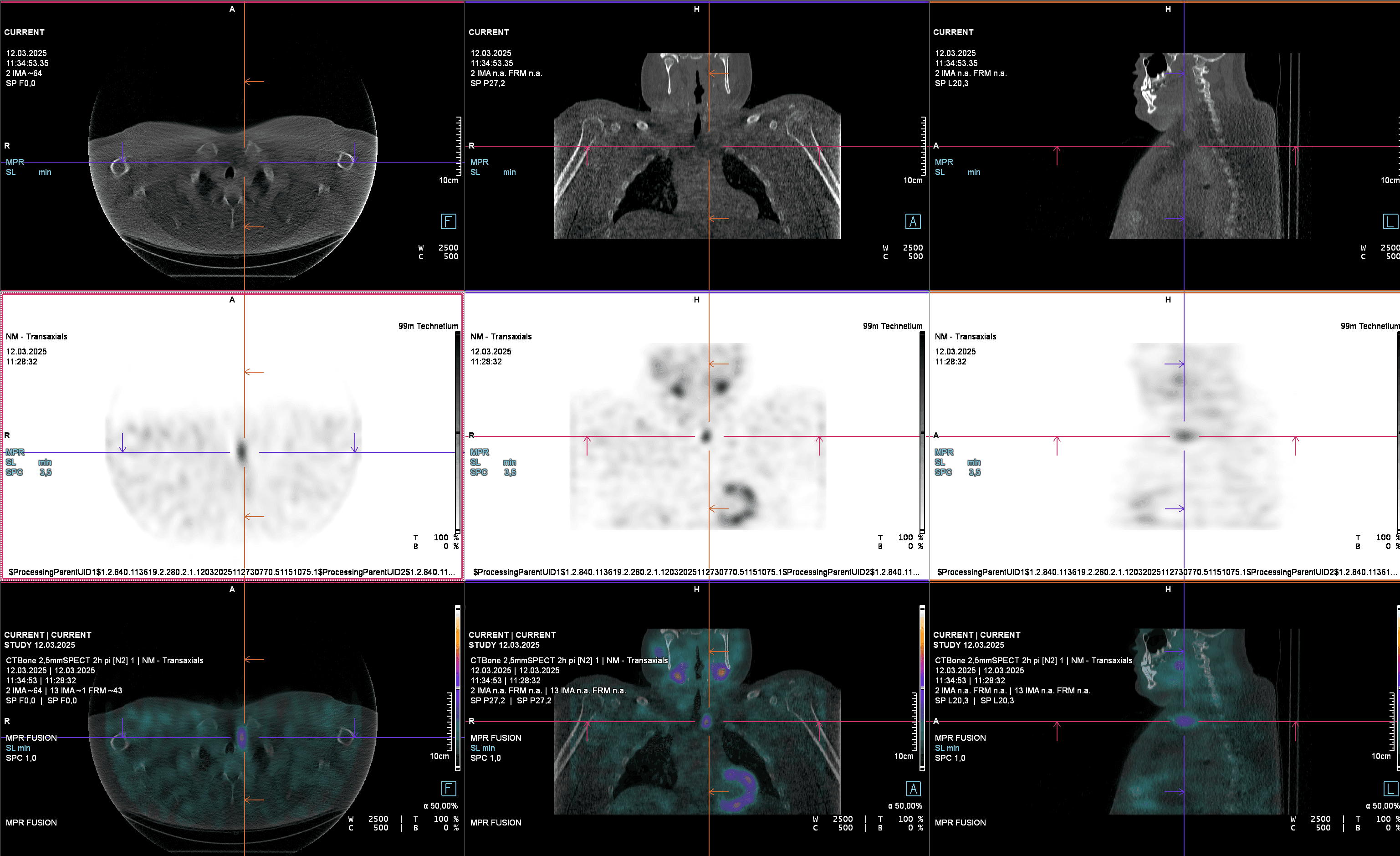
Parathyroid scintigraphy
Parathyroid scintigraphy localizes an overactive parathyroid adenoma that increases the calcium level. Accurate detection allows precise and minor neck surgery.

Parathyroid scintigraphy
Parathyroid scintigraphy localizes an overactive parathyroid adenoma that increases the calcium level. Accurate detection allows precise and minor neck surgery.

Lung scintigraphy (V/Q scan)
Pulmonary scintigraphy can be used to painlessly detect or rule out an embolism. The examination is carried out without iodine-containing contrast medium and is therefore gentle on kidneys, hyperthyroidism and allergy sufferers.

Lung scintigraphy (V/Q scan)
Pulmonary scintigraphy can be used to painlessly detect or rule out an embolism. The examination is carried out without iodine-containing contrast medium and is therefore gentle on kidneys, hyperthyroidism and allergy sufferers.

Renal scintigraphy (MAG3 & DMSA)
Renal scintigraphy measures separately how well each kidney filters and whether urine builds up. This allows a one-sided functional weakness or obstruction of the outflow to be detected long before creatinine levels rise.

Renal scintigraphy (MAG3 & DMSA)
Renal scintigraphy measures separately how well each kidney filters and whether urine builds up. This allows a one-sided functional weakness or obstruction of the outflow to be detected long before creatinine levels rise.

Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy
Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy – Accurate Diagnosis of Gastroparesis and Dumping Syndrome Gastric emptying scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging test that tracks the movement of a radioactively labeled test meal from the stomach into the small intestine. By capturing multiple images over a set period, it provides objective measurements of whether gastric emptying is delayed (gastroparesis) or accelerated (dumping syndrome). The procedure is painless, well-tolerated, and serves as a key diagnostic tool for planning targeted treatment of gastric motility disorders.

Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy
Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy – Accurate Diagnosis of Gastroparesis and Dumping Syndrome Gastric emptying scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging test that tracks the movement of a radioactively labeled test meal from the stomach into the small intestine. By capturing multiple images over a set period, it provides objective measurements of whether gastric emptying is delayed (gastroparesis) or accelerated (dumping syndrome). The procedure is painless, well-tolerated, and serves as a key diagnostic tool for planning targeted treatment of gastric motility disorders.
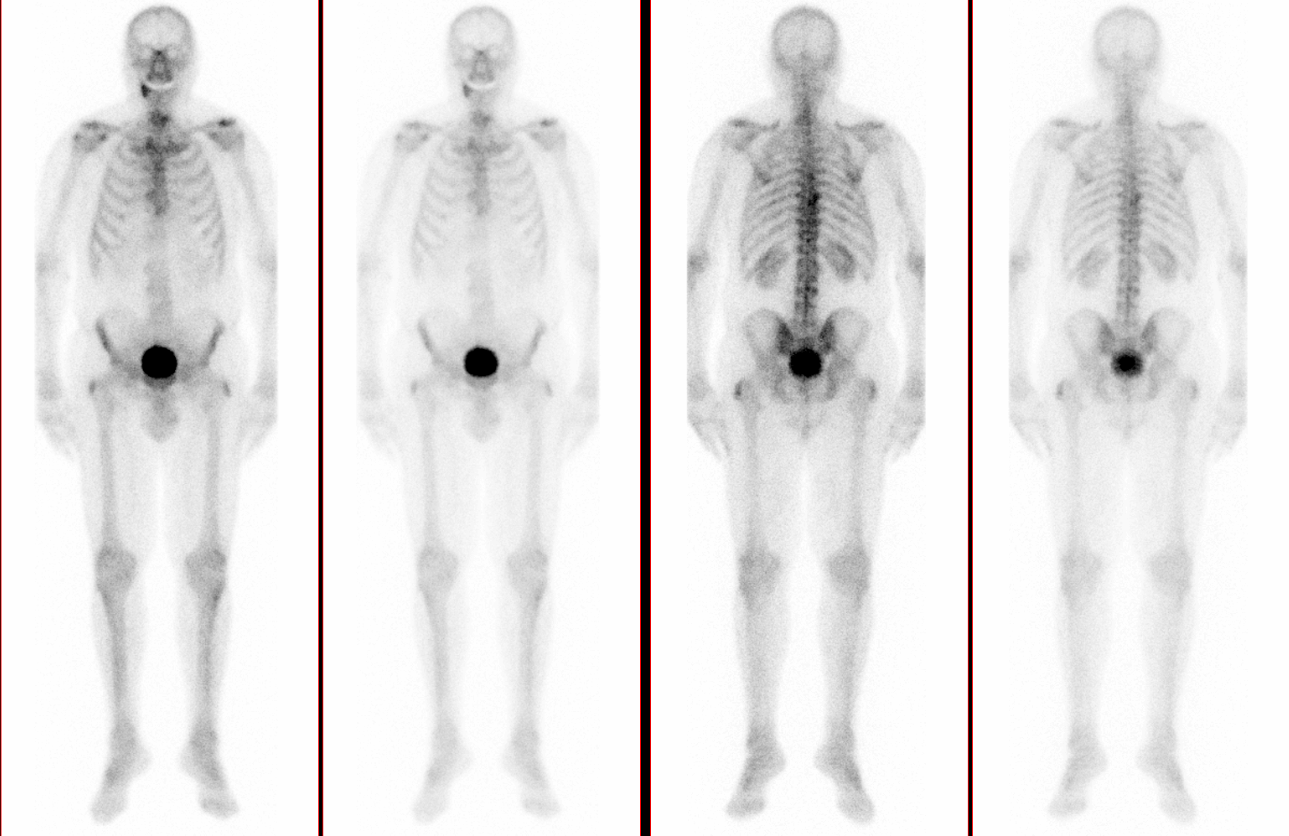
Bone Scintigraphy
Bone Scintigraphy – Whole-Body Imaging for Bone Metastases, Fractures, and Prosthesis Loosening Bone scintigraphy (also called skeletal scintigraphy) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that visualizes the metabolic activity of the entire skeleton.

Bone Scintigraphy
Bone Scintigraphy – Whole-Body Imaging for Bone Metastases, Fractures, and Prosthesis Loosening Bone scintigraphy (also called skeletal scintigraphy) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that visualizes the metabolic activity of the entire skeleton.

Sentinel Lymph Node Scintigraphy
Sentinel Lymph Node Scintigraphy – Precision Guidance in Cancer Surgery Sentinel lymph node scintigraphy (also called sentinel node mapping) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that identifies the first lymph node in the drainage area of a tumor. This “sentinel node” acts as the first filter where cancer cells may spread.

Sentinel Lymph Node Scintigraphy
Sentinel Lymph Node Scintigraphy – Precision Guidance in Cancer Surgery Sentinel lymph node scintigraphy (also called sentinel node mapping) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that identifies the first lymph node in the drainage area of a tumor. This “sentinel node” acts as the first filter where cancer cells may spread.

Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy (Tektrotyd®)
Targeted Imaging for Neuroendocrine Tumors Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy is a specialized nuclear medicine imaging technique used in the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors (NET). These tumors typically express somatostatin receptors on their surface. By injecting a small amount of radioactive somatostatin analogue (e.g., Tektrotyd®), tumors and their metastatic spread can be visualized with high precision.

Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy (Tektrotyd®)
Targeted Imaging for Neuroendocrine Tumors Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy is a specialized nuclear medicine imaging technique used in the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors (NET). These tumors typically express somatostatin receptors on their surface. By injecting a small amount of radioactive somatostatin analogue (e.g., Tektrotyd®), tumors and their metastatic spread can be visualized with high precision.
In good hands
Our Doctors

Dr. med. Volker Stark

Prof. Dr. med. Sebastian Lehner

Dr. Manuel Unterthiner
Competency

Dr. Peter Hildebrand
Competency

Dr. Maximilian Puille
Competency

Eva Wirthgen-Beyer
Competency

Dr. Wolfram Schneider
Competency

Dr. Carsten Altehöfer
Competency

Dr. Jan Stefan Schmid
Competency

Ciobotaru, Anton Bogdan
Competency

Dr. med. Marcus Middendorp

Elena Steingart
Competency

PD Dr. Franziska Dekorsy
Competency

Dr. Maria Hategan
Competency
Locations
Find a location near you
Your wellness, just a step away
Easily book your appointment online
Choose the time, location, and service you need